Ethereum Treasury Company: Disruptor or Builder of the On-chain Ecosystem?
Although it is currently in an accumulation phase, increased on-chain participation may enhance Ethereum liquidity and security while also increasing its exposure to corporate fund risk.
Original Article Title: Exploring the On-Chain Effects of ETH Treasury Companies
Original Article Author: Tanay Ved, Coin Metrics
Original Article Translation: Saoirse, Foresight News
Key Points
· The digital asset reserves focused on Ethereum are rapidly expanding, accumulating 2.2 million ETH in just two months (1.8% of the total supply), causing a supply-demand imbalance.
· These treasury funds are adopting an active on-chain strategy, planning to deploy funds through staking and DeFi to boost returns while supporting network security and liquidity.
· Although still in the accumulation phase, higher on-chain participation could enhance Ethereum's liquidity and security while increasing its exposure to corporate treasury risks.
The Rise of Digital Asset Treasuries
Digital Asset Treasuries (DATs), referring to listed companies that hold crypto assets such as Bitcoin or Ethereum on their balance sheets, have become a new market access channel. The launch of spot ETFs in 2024 unlocked the demand from investors unable to hold BTC and ETH directly through custody. Similarly, digital asset treasuries provide investors with exposure to these assets and their ecosystems through publicly traded stocks, with the ability to strategically raise and allocate funds.
We have previously delved into Michael Saylor's "Playbook," where by issuing stocks and convertible bonds, he accumulated over 628,000 bitcoins (2.9% of Bitcoin's total supply). Numerous global companies have followed suit, from Marathon Digital to Japan's Metaplanet, all providing shareholders with an amplified or "leveraged" Bitcoin exposure. Now, this model is expanding to other ecosystems, with many entities competing to increase their holding of ETH in corporate treasuries.
While the goal of increasing shareholder exposure to the underlying asset remains unchanged, there is a fundamental difference between Ethereum treasuries and Bitcoin treasuries: the former can leverage Ethereum's staking and DeFi ecosystem. This possibility enables higher returns through Ethereum's native yield and effective on-chain capital allocation. In this article, we will analyze the dynamic impact of Ethereum treasuries on the Ethereum supply and explore the potential effects of these large institutions entering the on-chain space.
Supply Dynamics: Race for 5% of the Supply
Since July of this year, the Ethereum digital asset reserve has accumulated a total of 2.2 million ETH, representing almost 1.8% of the current ETH total supply. Currently, there are 5 major players in this space, which have raised funds through methods such as public offerings or private investment in public equity (PIPE) by listed companies to allocate capital and enhance the value of their held assets. As of August 11, the holdings of these entities are as follows:
· Bitmine Immersion Technologies: 1.15 million ETH, valued at approximately $4.8 billion
· SharpLink Gaming: 521,000 ETH, valued at approximately $2.2 billion
· The Ether Machine: 345,000 ETH, valued at approximately $1.4 billion
· Bit Digital: 120,000 ETH, valued at approximately $503 million
· BTCS Inc.: 70,000 ETH, valued at approximately $293 million
Bitmine Immersion Technologies is currently the largest corporate holder of ETH, with its holdings accounting for 0.95% of the total ETH supply, and is rapidly moving towards its established goal of accumulating and holding 5% of the circulating ETH supply. With changing market conditions, these companies have been able to build reserves at favorable costs, intensifying the competition to acquire a larger share of ETH.
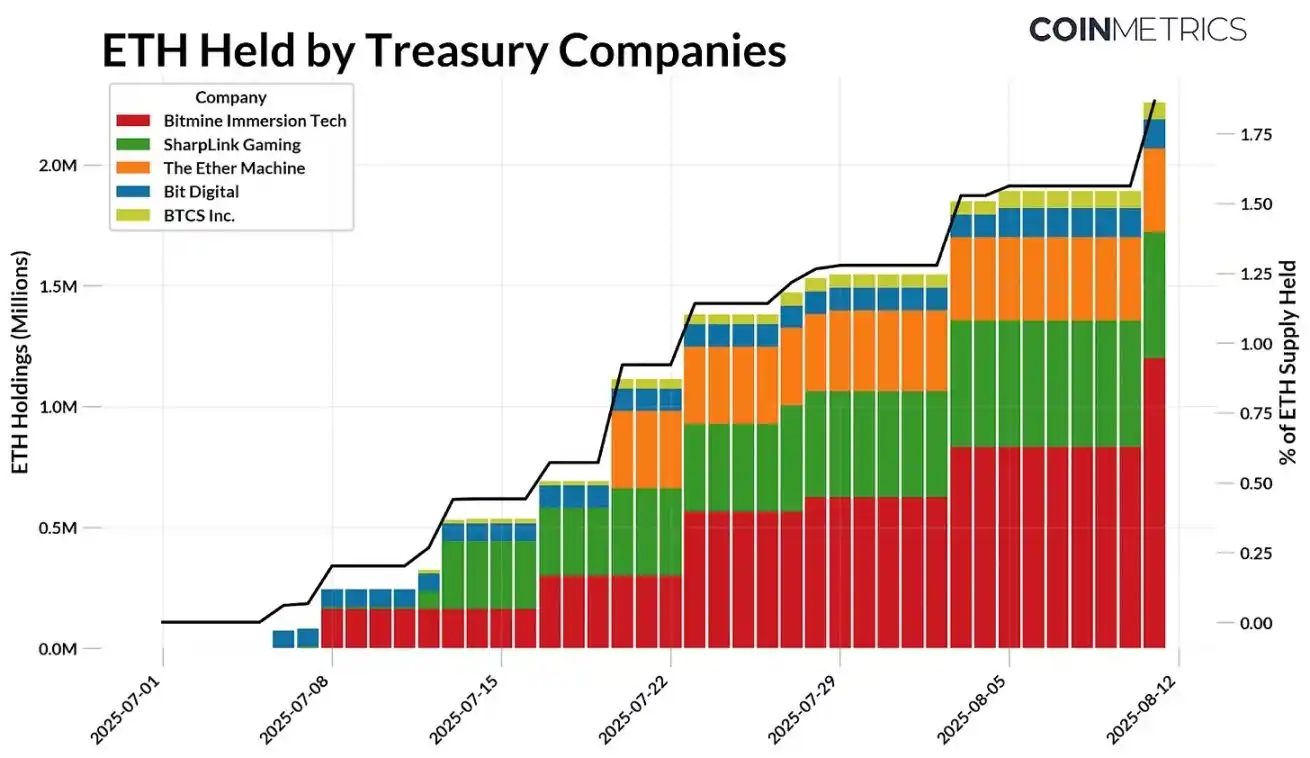
Source: Coin Metrics Network Data Pro and public documents (as of August 11, 2025)
Looking at Ethereum's issuance dynamics, this trend becomes even more significant. Ethereum's supply is regulated by a PoS mechanism, where newly minted ETH is allocated to validators, and a portion of transaction fees is burned, causing the net issuance to fluctuate between negative (deflationary) and positive (inflationary) values.
Since the September 2022 "merge," Ethereum has minted a total of 2.44 million ETH, burned 1.98 million ETH, resulting in a net issuance of 454,300 ETH. Since July of this year, the Ethereum Treasury Company has accumulated 2.2 million ETH, far exceeding the net issuance during the same period. Bitcoin's fixed supply cap and halving mechanism directly reduce its new issuance, while Ethereum's supply is dynamic and currently in an inflationary state. Considering Ethereum's market cap is about 1/4.5 of Bitcoin's, the scale and speed of recent demand are more worthy of attention.
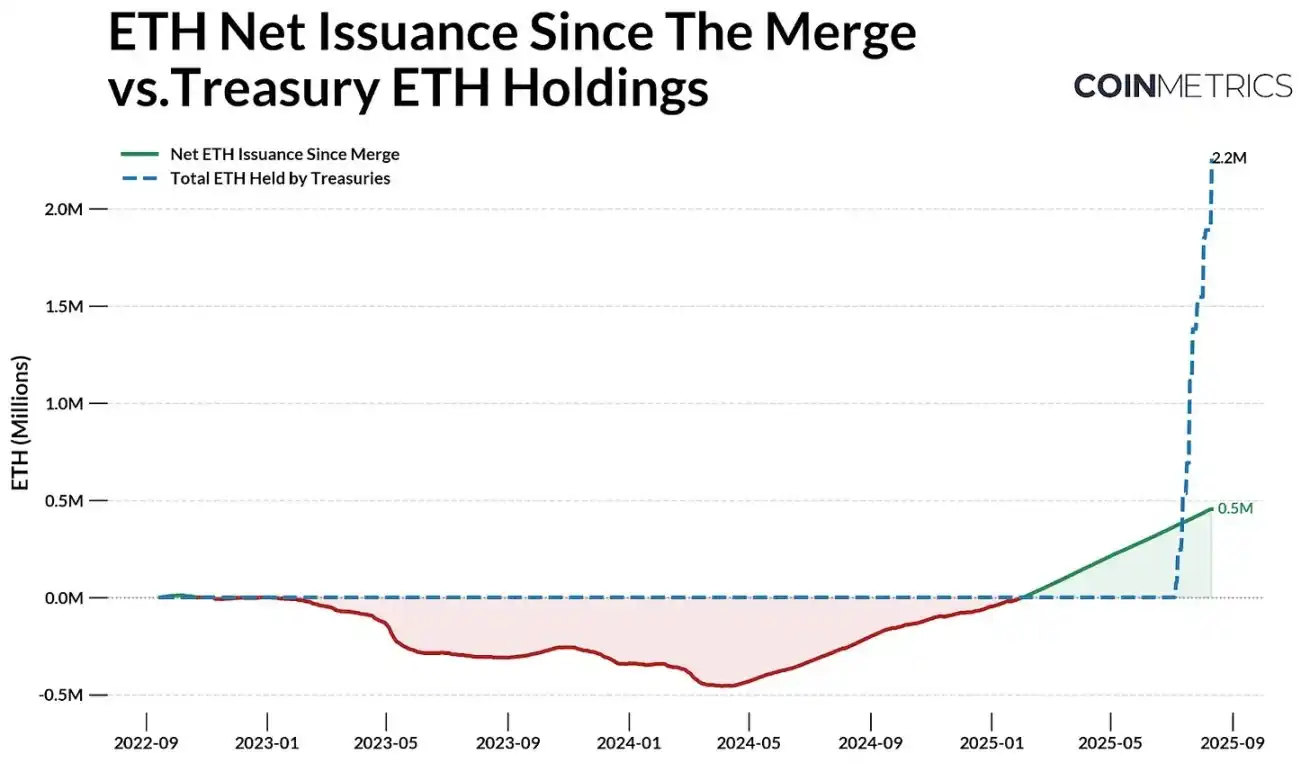
Source: Coin Metrics Network Data Pro and public documents
Considering the increasing inflow of funds into Ethereum ETFs in recent months, this supply-demand imbalance becomes more prominent. Overall, apart from the 29% of ETH staked in the consensus layer and the 8.9% of ETH held in other smart contracts, these instruments are continuously absorbing 107.2 million ETH from Ethereum's free float supply (market available supply). Therefore, the continued accumulation by reserves and ETFs could amplify the price sensitivity to new demand.
Ecosystem Impact: Staking, DeFi, and On-Chain Activity
While most ETH treasuries are still in the accumulation phase, a portion of their funds may eventually go on-chain. Unlike Bitcoin's treasury's relatively passive approach, these companies plan to leverage Ethereum's staking and DeFi infrastructure to enhance risk-adjusted returns and maximize the efficiency of their holdings. This transition is already underway: SharpLink Gaming is staking a significant portion of its holdings, BTCS Inc. is earning through Rocket Pool, and other companies like The Ether Machine and ETHZilla are also preparing for a more active on-chain management.
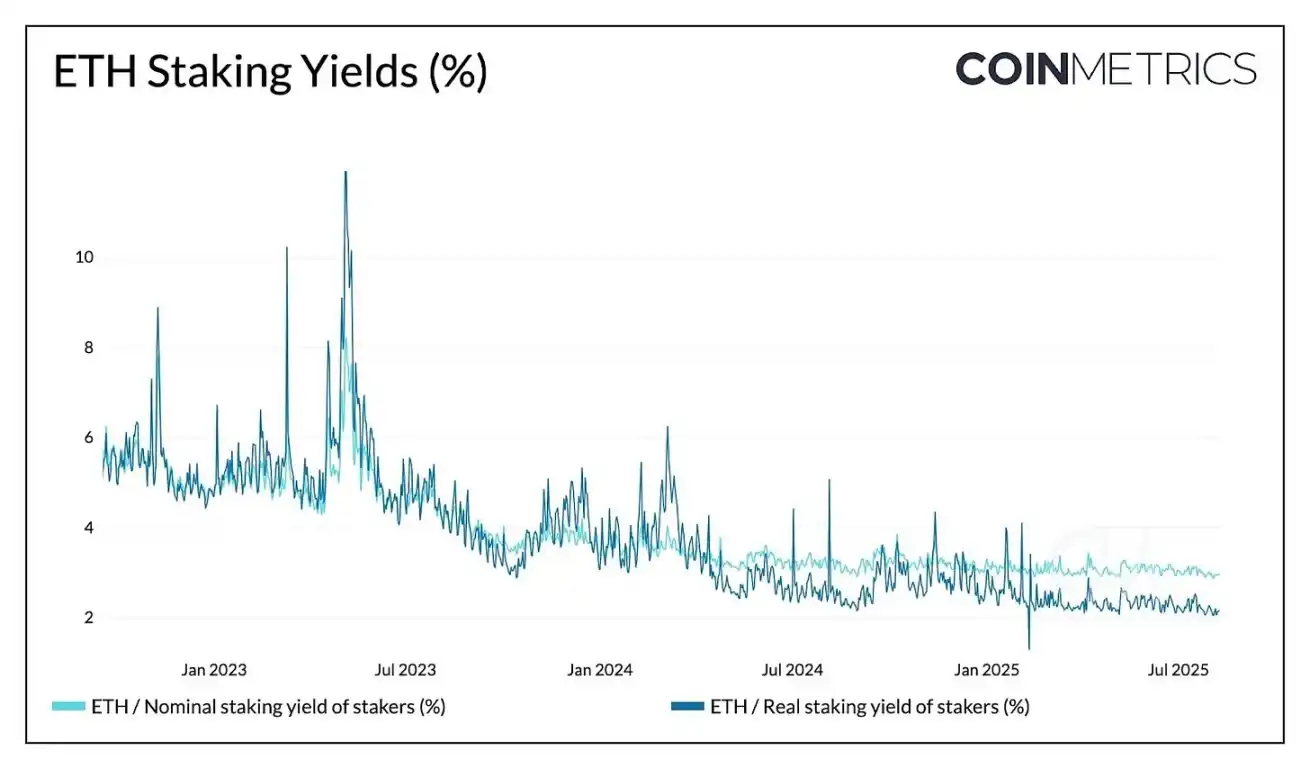
Source: Coin Metrics Network Data Pro
Currently, by providing staking rewards for network security, Ethereum can offer a 2.95% nominal yield and a 2.15% real (adjusted for inflation) yield. This not only can drive price appreciation for the underlying asset but also provides a stable income stream for treasury companies. For example, if 30% of the 2.2 million ETH held by treasury companies is staked at the current nominal yield rate of around 3% and ETH is priced at $4,000, it can generate approximately $79 million in annual revenue. While a substantial inflow of funds into staking may decrease the yield rate, the impact is relatively mild due to Ethereum's reward rate decreasing gradually as the staked amount increases.
Corporate treasuries primarily engage through two methods: running their own validation nodes and utilizing liquidity staking protocols. The U.S. SEC has clarified that liquidity staking protocols are not considered securities, allowing companies to stake through third-party entities like Lido, Coinbase, or RocketPool and receive "liquidity" proof-of-stake tokens as a reward.
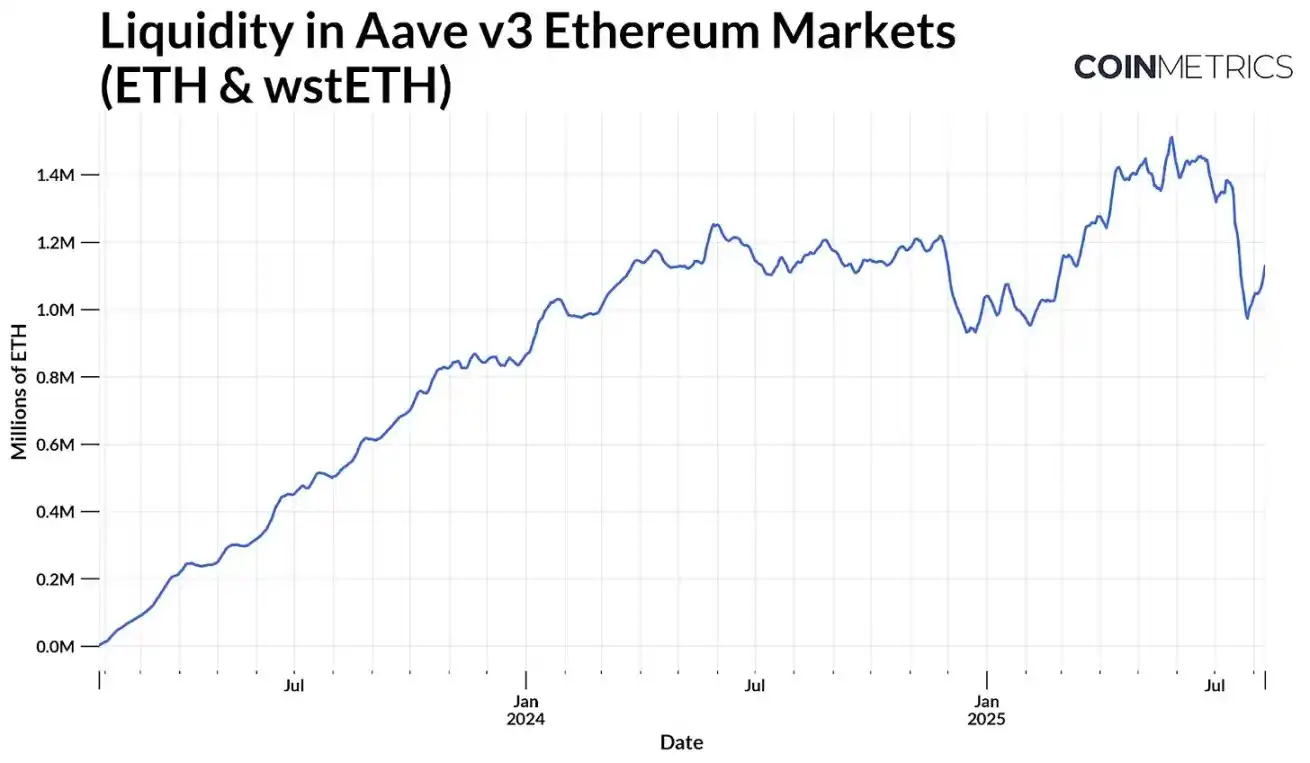
Source: Coin Metrics ATLAS
Despite additional risks, tokens like Lido's stETH are widely used in DeFi for staking and lending, or to earn additional yield on top of the base staking APY in a capital-efficient manner. For example, in Aave v3, assets like ETH and liquid staking tokens such as stETH form a large pool of available liquidity (assets available for borrowing). This liquidity pool has now grown to around 1.1 million ETH, and inflows of reserve capital could further expand the pool size, enhancing market liquidity while boosting returns.
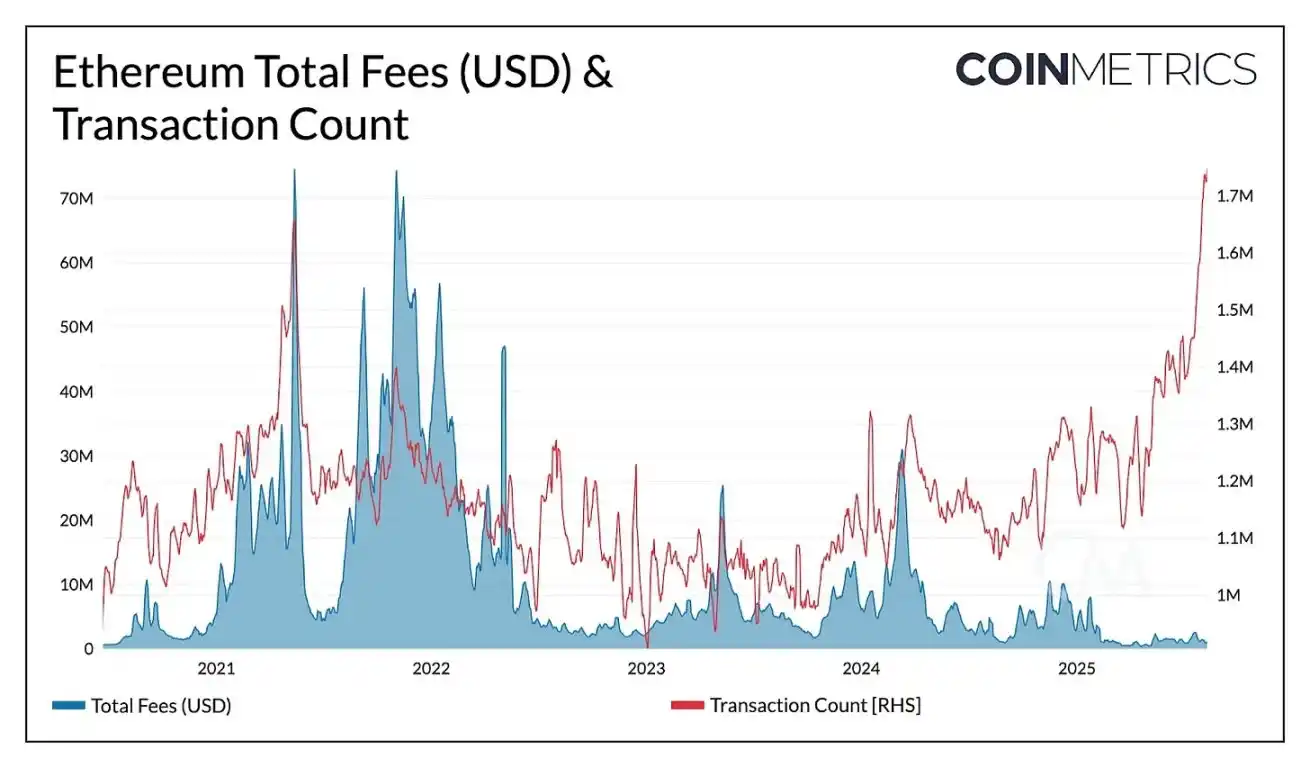
Source: Coin Metrics Network Data Pro
Although Ethereum's mainnet transaction volume has surpassed its historical records (ranging from 1.7 to 1.9 million daily transactions), recent gas limit increases and block capacity expansions have alleviated network congestion, redirecting some activity to Layer 2 solutions. As a result, total fees remain low compared to recent years. If corporate treasury funds make a large-scale entry onto the chain, high-value transactions on Ethereum L1 could drive an increase in overall block space demand and fee revenue, potentially creating a positive feedback loop between reserve activity, liquidity, and on-chain usage.
Linking Corporate Treasury Performance to On-Chain Health
As the on-chain footprint of publicly traded Ethereum treasury corporations continues to grow, the impact of their financial performance on Ethereum's long-term network health becomes increasingly significant, bridging off-chain corporate performance with potential on-chain repercussions. Large-scale long-term holdings can reduce circulating supply, increase credibility, and boost on-chain liquidity, but centralization, leverage, and operational risks mean that corporate-level issues could propagate to the network.
Impact of Large ETH Reserve Holdings on the Chain
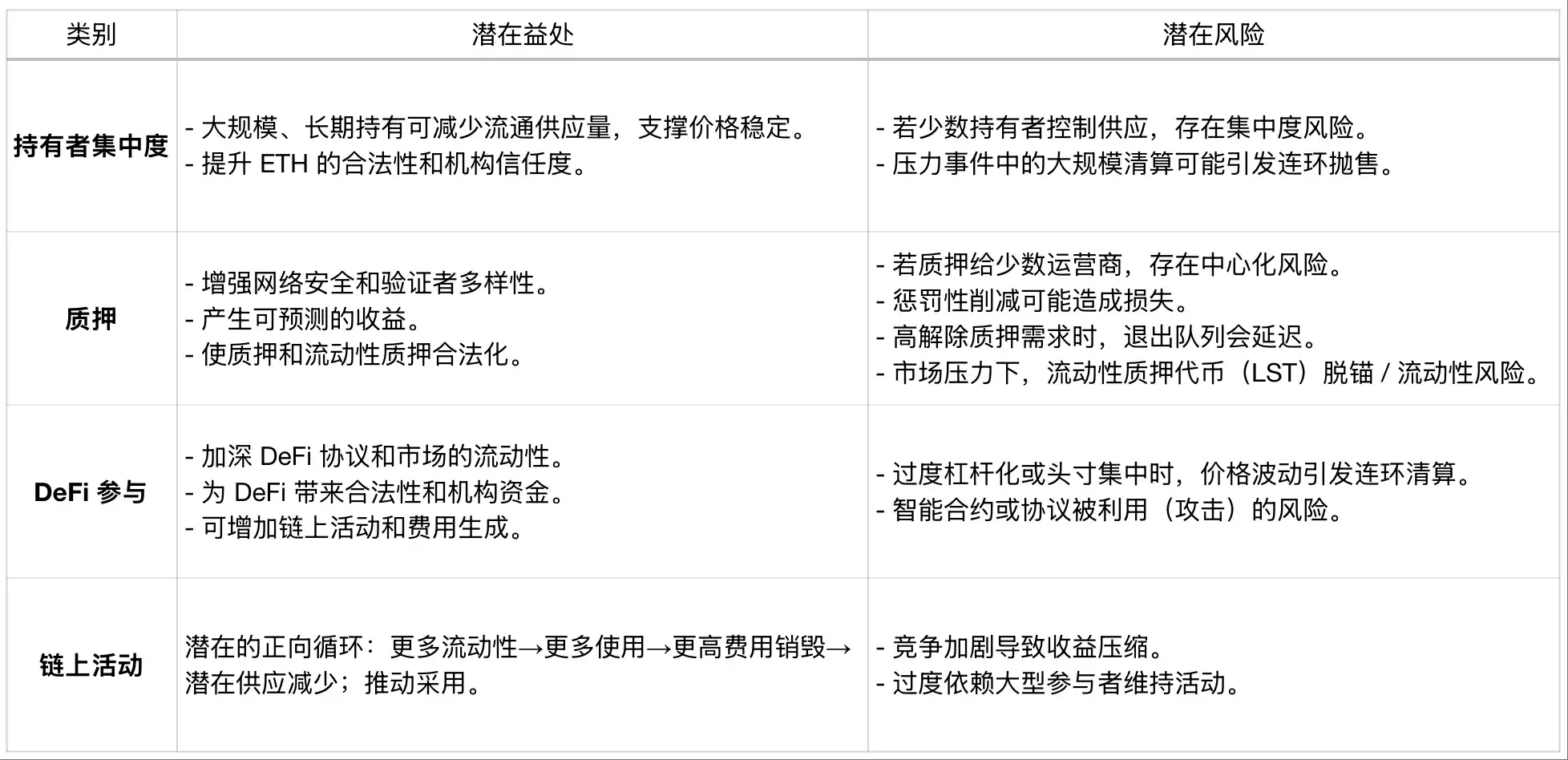
While these are network-level considerations, corporate treasuries themselves are also subject to market forces and investor sentiment. A strong balance sheet and sustained investor confidence can grow reserve holdings and enhance participation. Conversely, significant drops in asset prices, liquidity crunches, or excessive leverage may lead to ETH selling or reduced on-chain activity.
Treasury Performance-Related Metrics
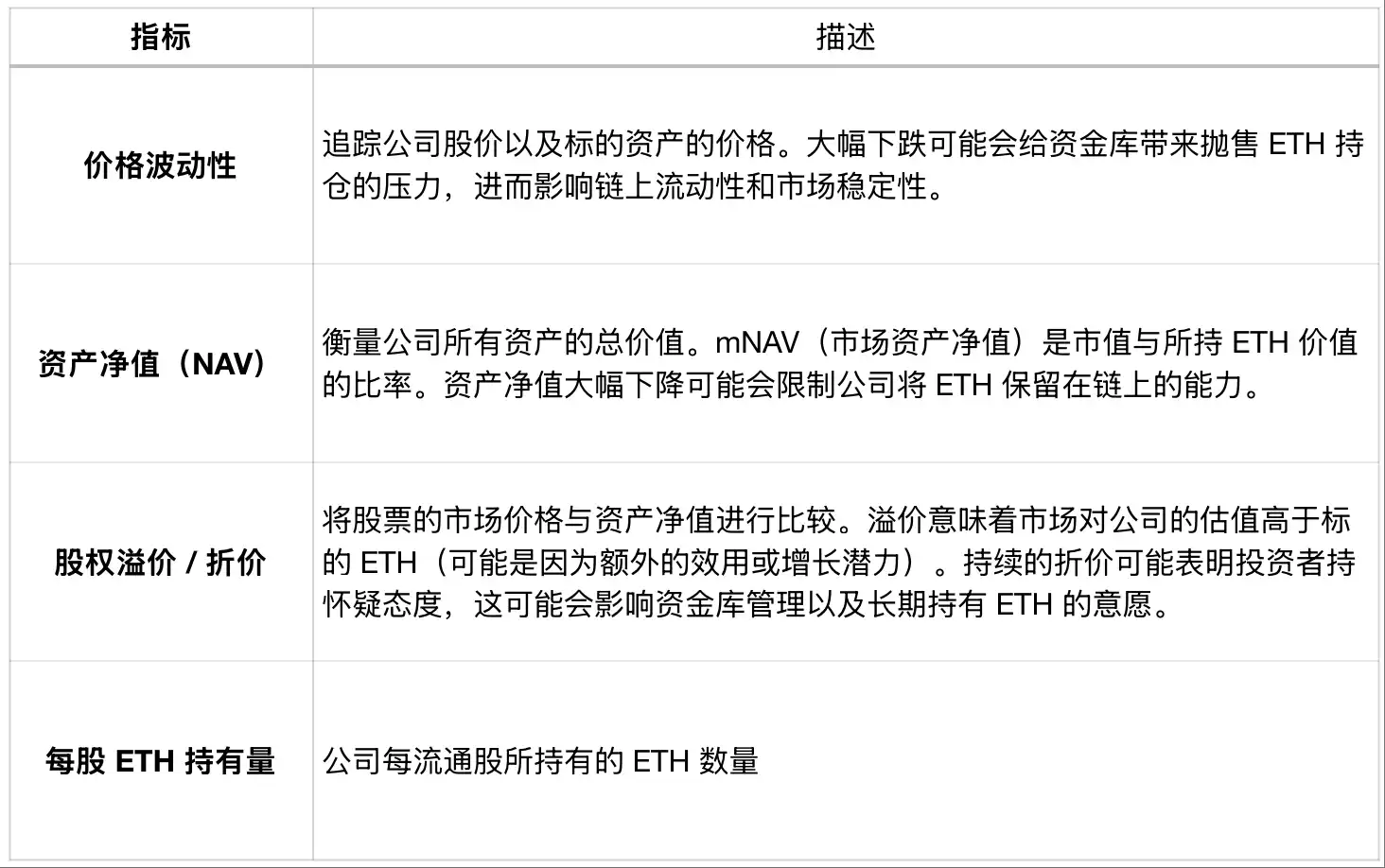
The metrics describe the price volatility tracking the company's stock price as well as the price of the underlying asset. A significant drop may bring selling pressure to the treasury, affecting on-chain liquidity and market stability. Net Asset Value (NAV) measures the total value of all company assets. mNAV (market NAV) is the ratio of market cap to the value of held ETH. A sharp drop in asset value may restrict the company's ability to keep ETH on-chain. Equity Premium / Discount compares the stock's market price to the asset's net value. A premium means the market values the company higher than the underlying ETH (possibly due to additional utility or growth potential). Continued discount may indicate investor skepticism, which could affect treasury management and willingness to hold ETH long-term. ETH per Share is the amount of ETH held per outstanding share.
By tracking the network-level impact and the financial health of these companies, market participants can better predict how corporate treasury actions may impact Ethereum's supply dynamics and overall network health.
Conclusion
The rapid rise of corporate Ethereum treasuries reflects Ethereum's attractiveness as a reserve asset and on-chain revenue source. Its growing influence may increase liquidity, active network participation, but also come with risks related to leverage, financing, and capital management. As off-chain factors (such as stock performance, debt repayment) become increasingly linked to on-chain activities, these factors may quickly impact the chain. As these institutions' scale grows, tracking their balance sheet health and on-chain activity will be key to understanding their impact.
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
Bitget Trading Club Championship (Phase 4)—Grab a share of 50,000 BGB, up to 500 BGB per user!
Onchain Challenge (Phase 14) — Trade and share 100,000 BGB in airdrops

Bitget to support loan and margin functions for select assets in unified account
Up to 50% BGB rebates: Deposit & buy crypto with VND today!
